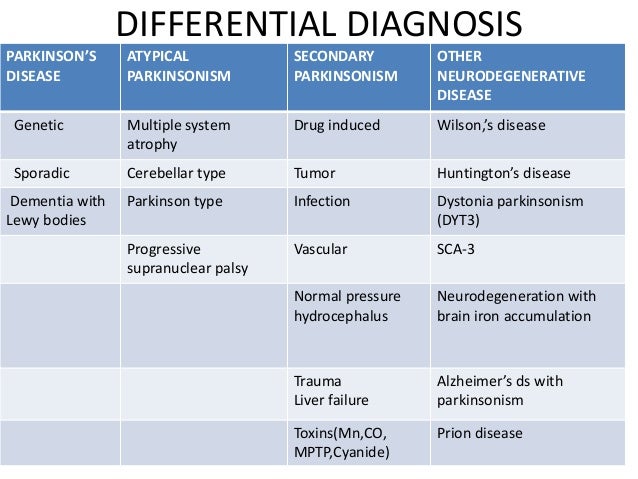
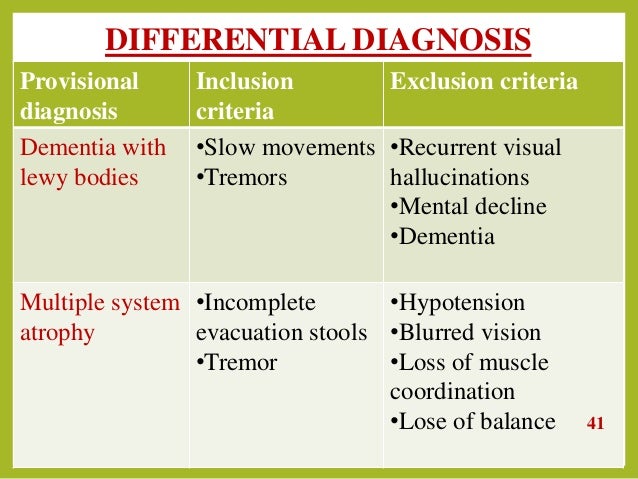
Parkinson's Disease Differential Diagnosis
Parkinson's disease differential diagnosis. Progressive supranuclear palsy -. In addition with the development of invasive therapies and novel disease-specific therapies strategies for patient enrichment in trial populations are of growing importance. Parkinsons Disease Parkinsons disease is the most com-mon identifiable syndrome that can be diagnosed in the context of Parkinsonism.
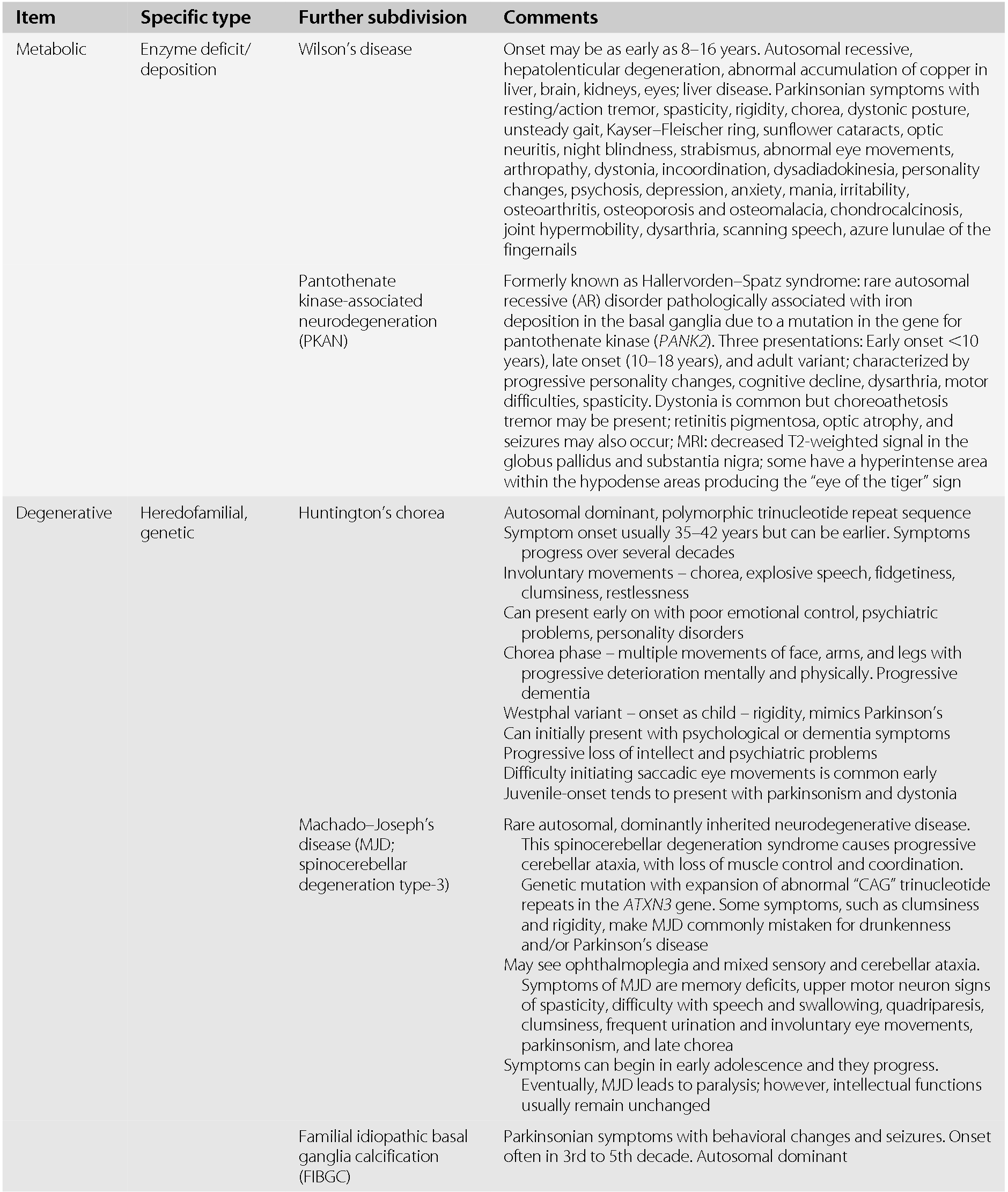
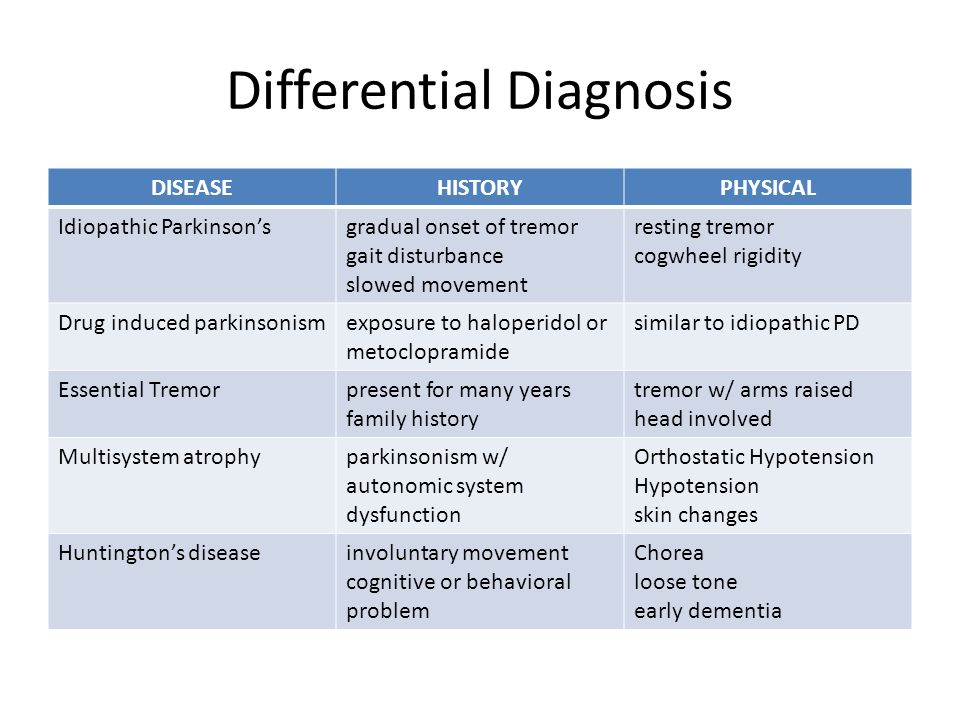
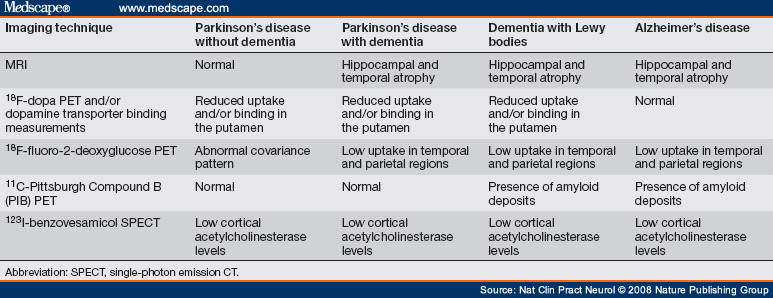
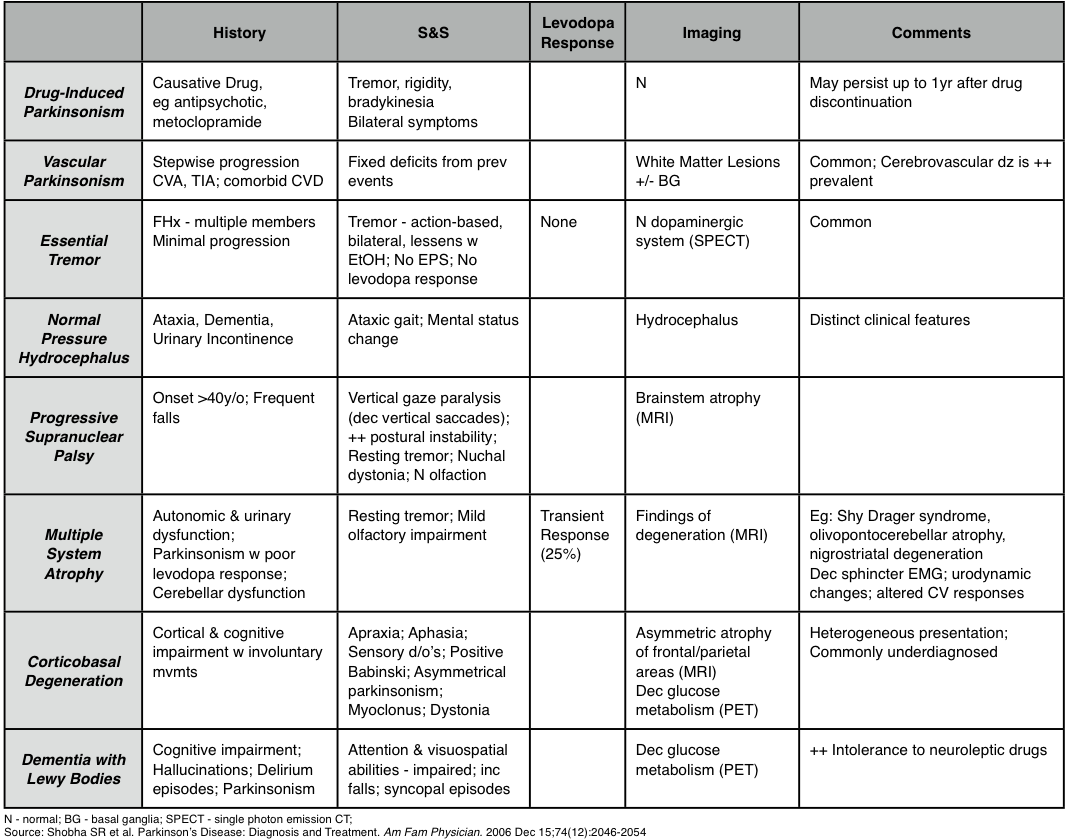
The most important clues to the diagnosis of Parkinsons disease include of course elements of Parkinsonism usually 2 of 3 of the cardinal featuresbradykinesia tremor cogwheel rigidity. Parkinsons Disease Parkinsons disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized pathologically by loss of dopaminergic cells in the substantia nigra and by the presence of Lewy bodies. Such diagnostic inaccuracy is largely due to failure to recognize atypical parkinsonian disorders including multiple system atrophy MSA progressive supranuclear palsy PSP corticobasal degeneration CBD and dementia with Lewy bodies DLB.
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosi s of Parkinson s Disease 3 onset. The Differential Diagnosis of Parkinsons Disease Parkinsons disease PD is a common progressive neurodegenerative disease. Accurate differential diagnosis of parkinsonism is of paramount therapeutic and prognostic importance.
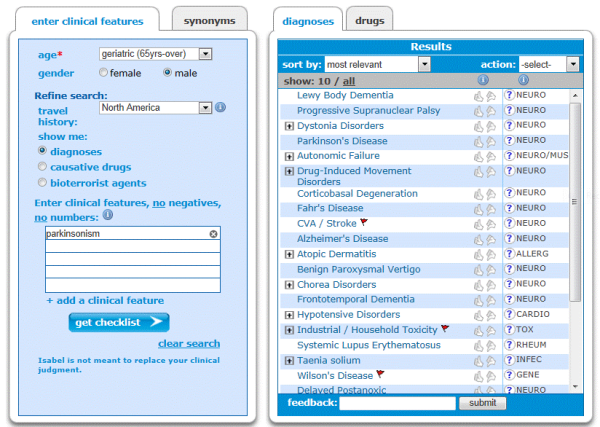
Diagnostic Considerations The most common tremor disorders are Parkinson disease and essential tremor. Lewy body dementia presents with dementia hallucinations fluctuating mental status. Most parkinsonian patients present with clinical clues to guide the neurologists diagnostic assessment.
On occasion the true bradykinesia of PD can be mistaken because the patient. When a patient presents with tremor. This differential diagnosis of Parkinsons disease includes.
Parkinson disease PD is the most common cause of parkinsonism and affects an estimated 329 per 100000 persons with roughly 50000 new cases diagnosed each year. Brain parenchyma sonography discriminates Parkinsons disease and atypical parkinsonian syndromes. Most commonly the patient presents with a unilateral resting tremor bradykinesia and rigidity and frequently nonmotor symptoms as well.
12 The cardinal symptoms of PD include bradykinesia rigidity and resting tremor with postural instability occurring as the disease progresses. Progressive supranuclear palsy presents with gaze palsies and early falls within 1 year of diagnosis.
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosi s of Parkinson s Disease 3 onset.
Progressive supranuclear palsy presents with gaze palsies and early falls within 1 year of diagnosis. In addition with the development of invasive therapies and novel disease-specific therapies strategies for patient enrichment in trial populations are of growing importance. There is often no rigidity or resting tremor and there may be an action tremor. Most parkinsonian patients present with clinical clues to guide the neurologists diagnostic assessment. Such diagnostic inaccuracy is largely due to failure to recognize atypical parkinsonian disorders including multiple system atrophy MSA progressive supranuclear palsy PSP corticobasal degeneration CBD and dementia with Lewy bodies DLB. Parkinsons Disease Parkinsons disease is the most com-mon identifiable syndrome that can be diagnosed in the context of Parkinsonism. Lewy body dementia presents with dementia hallucinations fluctuating mental status. Differential diagnosis of Parkinsonism Primary movement disorders Essential Tremor Primary Parkinsonian disorders Idiopathic Parkinsons disease PD Atypical Parkinsonism Parkinsons plus syndrome Progressive Supranuclear Palsy PSP Dementia with Lewy Bodies DLB Multiple System Atrophy MSA. On occasion the true bradykinesia of PD can be mistaken because the patient.
A prospective blinded study. These non-motor symptoms such as olfactory dysfunction or altered sleep behaviour have not yet been sufficiently recognized in structured diagnostic criteria but are likely to be included in the future. Differential diagnosis of Parkinsonism Primary movement disorders Essential Tremor Primary Parkinsonian disorders Idiopathic Parkinsons disease PD Atypical Parkinsonism Parkinsons plus syndrome Progressive Supranuclear Palsy PSP Dementia with Lewy Bodies DLB Multiple System Atrophy MSA. Walter U Niehaus L Probst T et al. 112 The Differential Diagnosis of Parkinsons Disease display small and cramped handwriting which becomes progressively smaller micrographia with a tendency of the sentence to fall off the line. Most commonly the patient presents with a unilateral resting tremor bradykinesia and rigidity and frequently nonmotor symptoms as well. A prospective blinded study.






































Post a Comment for "Parkinson's Disease Differential Diagnosis"