Osgood Schlatter Disease X Ray
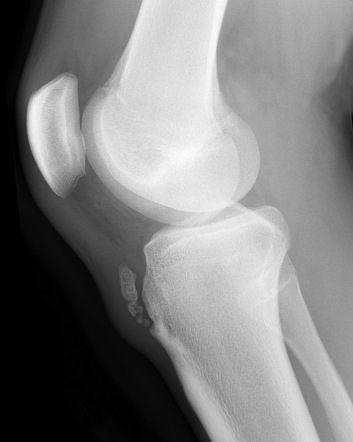
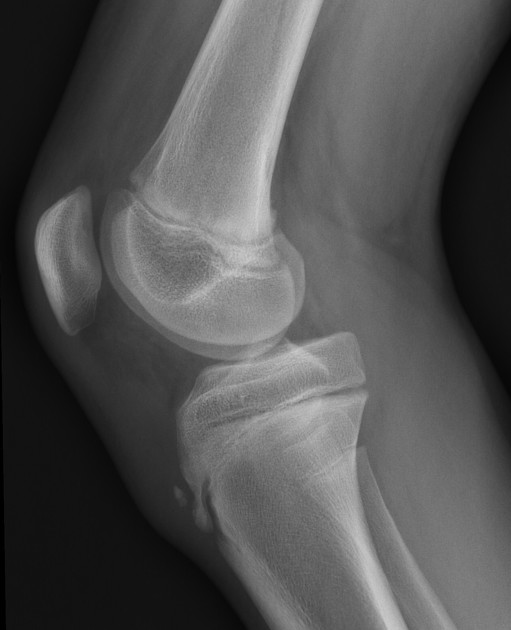
Osgood schlatter disease x ray. Osgood-Schlatter disease affects the upper part of your shin bone tibia due to the overuse of the quadricep muscles located on the front of your thigh. Asymtomatic - left Knee. It is a nontraumatic condition.
It occurs due to a period of rapid growth combined with a high level of sporting activity. OSD is type of juvenile traction osteochondritisOsteochondritis is a painful condition where the cartilage and bone in a joint is inflamedThe patients agegroup more common in late childhood or early adolescence sex more common in boys activity levels may represent an. Radiography of OSD.
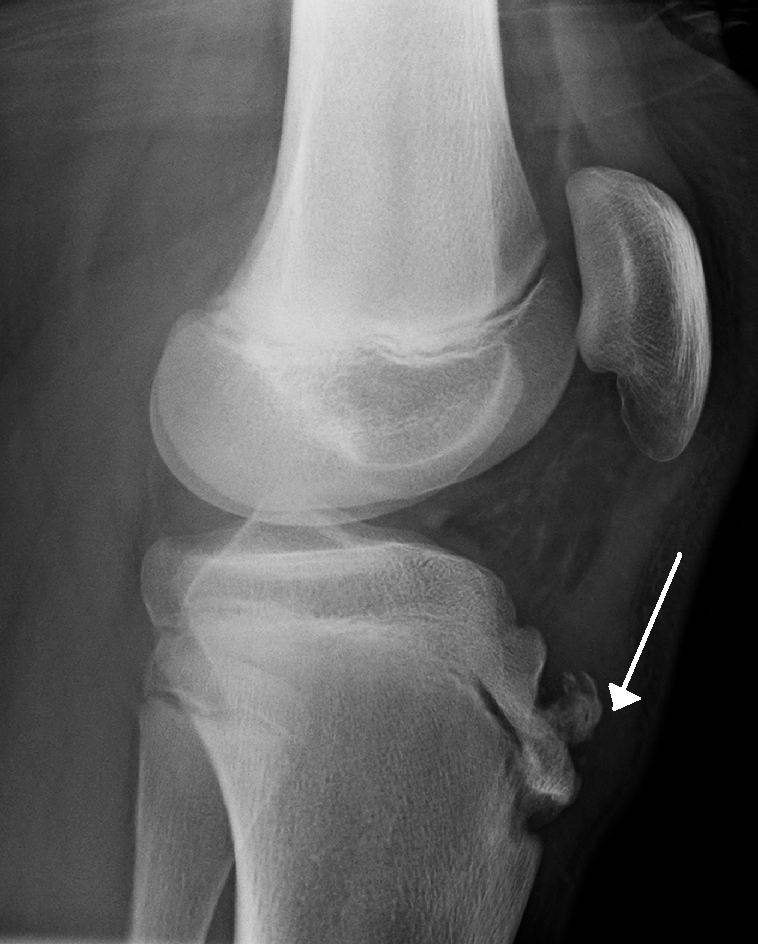
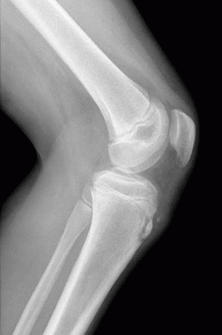
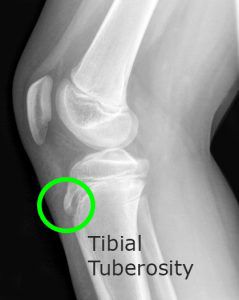
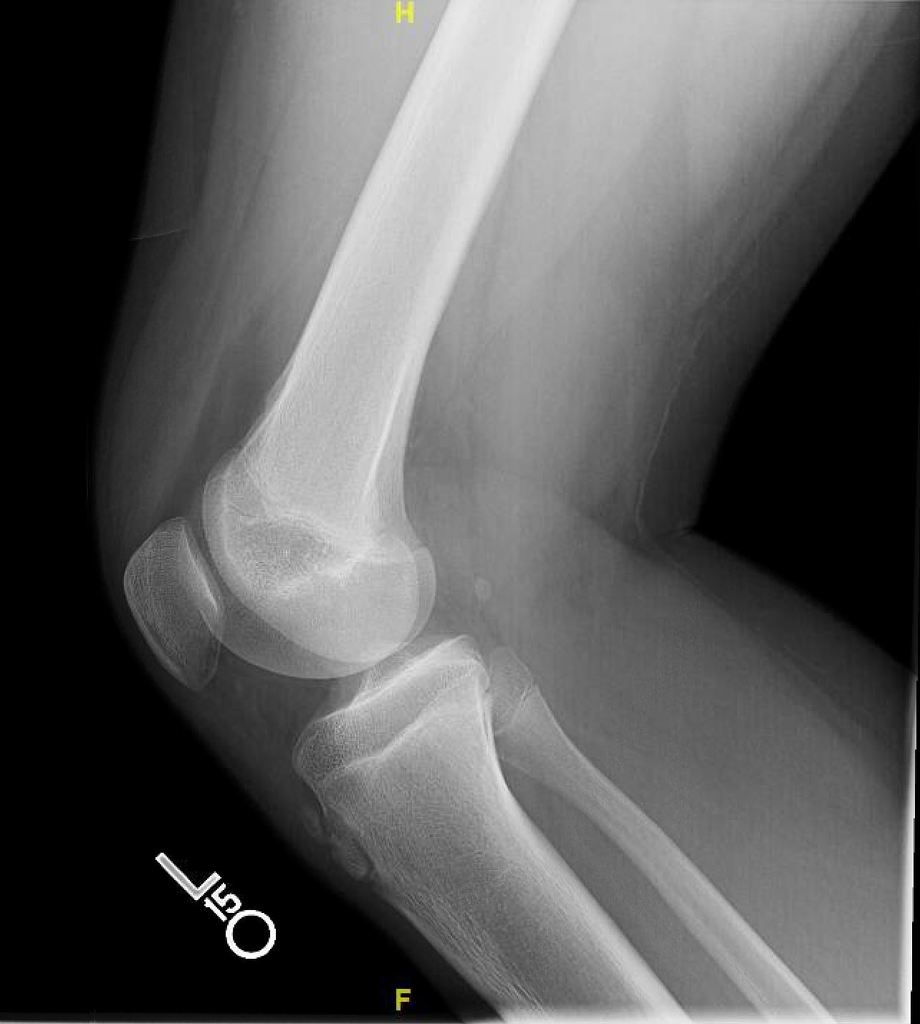
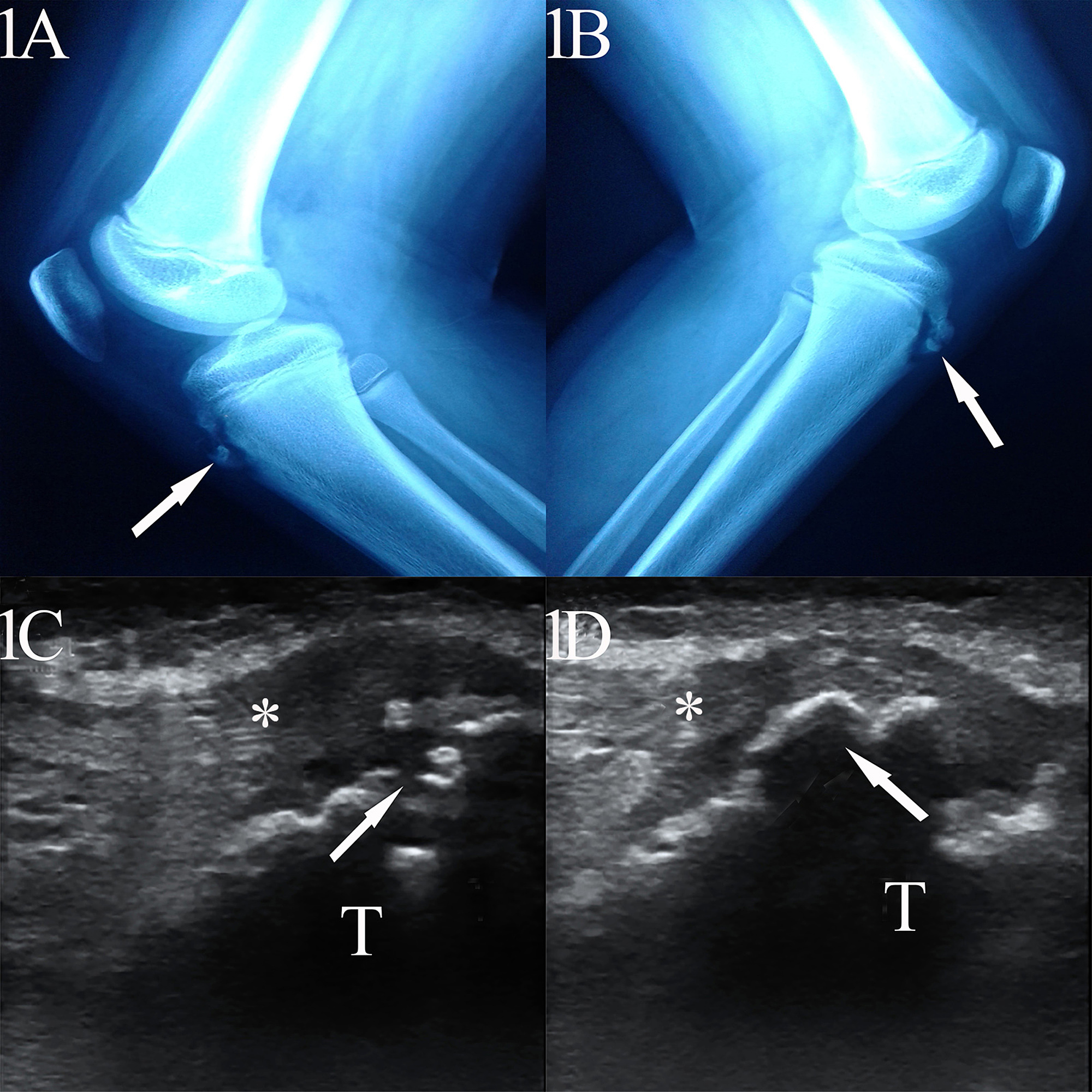
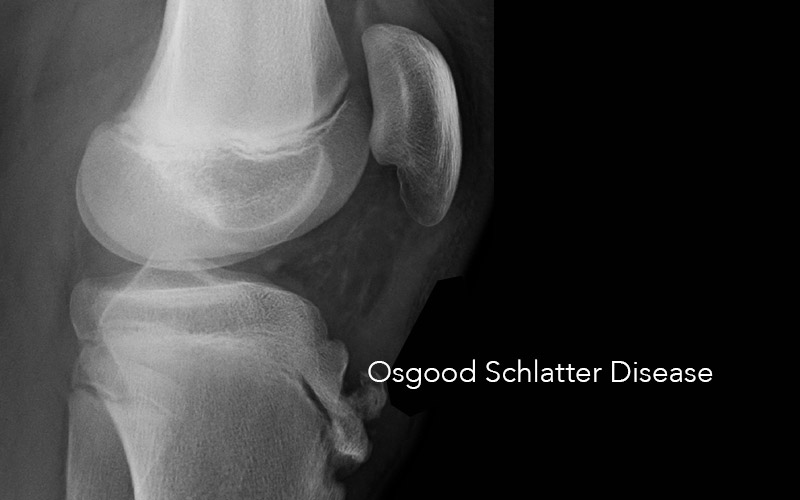
The blue arrow points at the prominent bone tibial tubercle. But sometimes X-ray of osgood schlatter disease. It results from an inflammation at the patellar tendon insertion on the anterior tibial tuberosity.
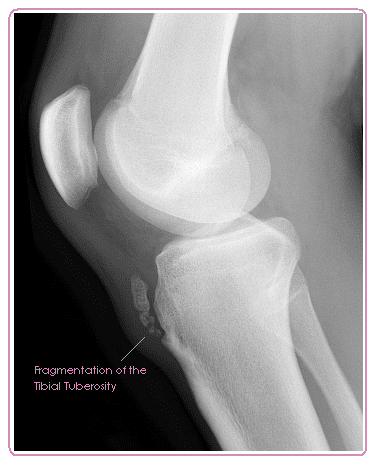
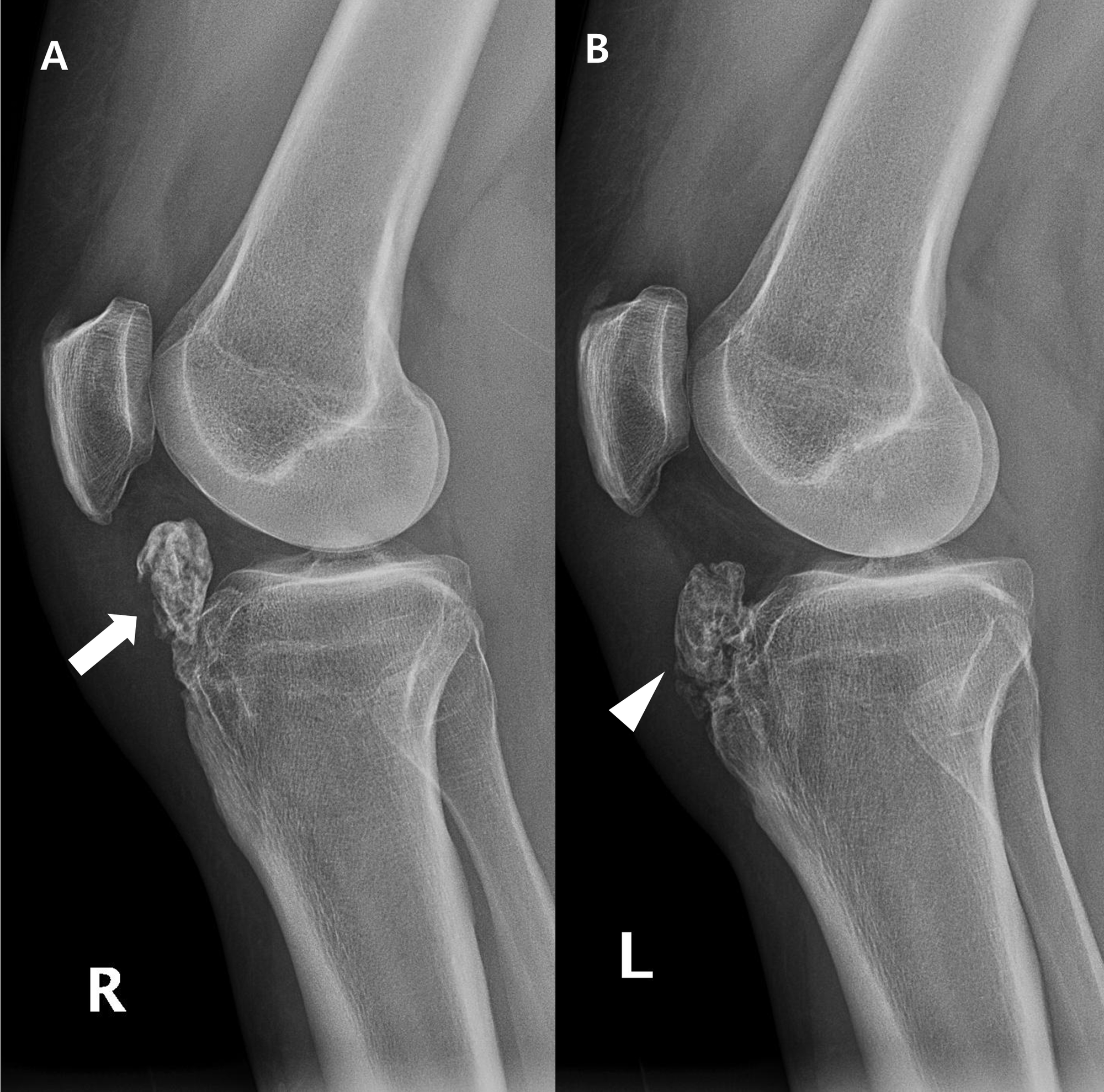
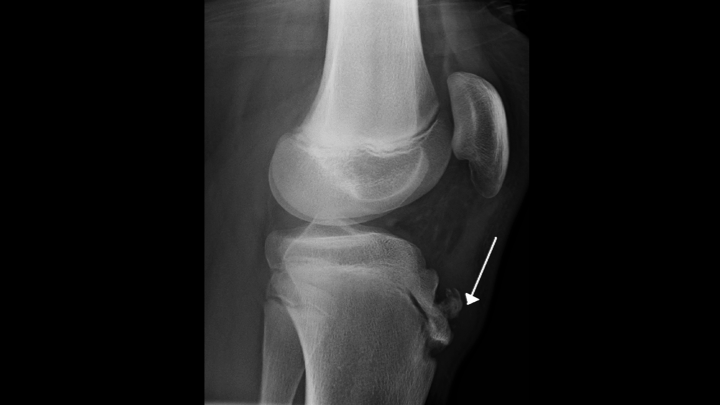
Lateral radiograph shows fragmentation and soft tissue swelling over the tibial tuberosity in favor of Osgood-Schlatter disease. Patients commonly complain of pain and soreness at the tibial tubercle while climbing stairs. Your doctor may choose to take an x-ray of your knee to look at the painful bump.
If undertaken knee X-ray in Osgood-Schlatter disease may be normal or may demonstrate anterior soft tissue swelling thickening of the patellar tendon fragmentation of the tibial tubercle or ossicle. Do not routinely X-ray the knee to confirm a diagnosis of Osgood-Schlatter disease. OsgoodSchlatter disease is a common cause of knee pain in physically active adolescents.
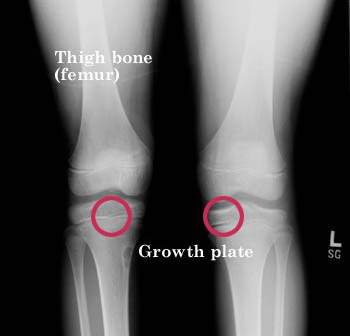
In adolescents the tibia is still growing. An MRI scan is usually not necessary for the diagnosis of Osgood-Schlatters disease. Ossification center s of tibial tubercle aka tuberosity usually fuse to each other and tibia at age 12 girls to 13 boys.
Osgood Schlatter disease is as much a clinical diagnosis as it is a radiographic diagnosis. Normal x-ray findings do not exclude the disease which is diagnosed.
Do not routinely X-ray the knee to confirm a diagnosis of Osgood-Schlatter disease.
OsgoodSchlatter disease is a common cause of knee pain in physically active adolescents. Lateral radiograph shows fragmentation and soft tissue swelling over the tibial tuberosity in favor of Osgood-Schlatter disease. Symptomatic - Right Knee. It results from an inflammation at the patellar tendon insertion on the anterior tibial tuberosity. Radiography of OSD. Patients commonly complain of pain and soreness at the tibial tubercle while climbing stairs. The disease is characterized by inflammationpain swelling and tendernessat the tibial tubercle. A clinical diagnosis Osgood-Schlatter disease is a common cause of knee pain in adolescents between 10-15. In adolescents the tibia is still growing.
Do not routinely X-ray the knee to confirm a diagnosis of Osgood-Schlatter disease. Overuse of the quadricep muscles can cause stress on the attachment of the patellar kneecap ligament to the upper part of the growing tibia. But sometimes X-ray of osgood schlatter disease. OSD is type of juvenile traction osteochondritisOsteochondritis is a painful condition where the cartilage and bone in a joint is inflamedThe patients agegroup more common in late childhood or early adolescence sex more common in boys activity levels may represent an. Patients commonly complain of pain and soreness at the tibial tubercle while climbing stairs. Ossification center s of tibial tubercle aka tuberosity usually fuse to each other and tibia at age 12 girls to 13 boys. An MRI scan is usually not necessary for the diagnosis of Osgood-Schlatters disease.


























Post a Comment for "Osgood Schlatter Disease X Ray"